Gravity meter S-99
Power Supply & Platform Control
Unit test points
Click here to get a PDF version
version of this document.
You need at least a multimeter to perform these tests;
an oscilloscope is, however, best.
1. Power supply test
The power supply has three testpoints, phase
A, B and C. These are the gyro spin motor
excitation voltages. The motor is 3-phase AC,
driven by 200 Hz sinusoids, 120║ phase shifted.
The phase voltages can be measured in two
ways, a) Neutral (0V) to Line, or b) Line to
Line.
1.1 Phase voltage
|
 1.1.1 Using multimeter. 1.1.1 Using multimeter.
Meter setup: AC. Measure between 0V and each phase, and
between phases. Also measure frequency, if the multimeter
has this capability.
TBD = To be determined.
|
1.1.2 Using oscilloscope.
Measure between 0V and each phase.
Note: Do not measure between phases by
attaching the probe's ground clip to one of the
phases - you risk making a short circuit if the
scope's ground is tied to power supply 0 V.
Instead make a differential measurement using two
probes, ground clips to 0V, and then subtract
ch.2 from ch.1.
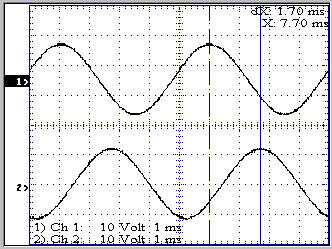
The figure on the right shows phase A and B.
Peak-to-peak value is approx 24 V. The phase
difference can be measured to (1.7ms/5ms)*360║ =
122║; the cursor readout is however not very
accurate, so this just indicates the 120║ phase
shift.
|
 |
| |
|
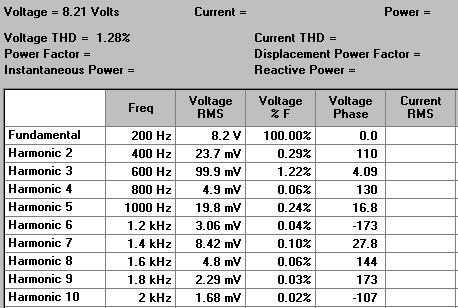 The signals are not "pure"
200 Hz sinusoids. If a spectral decomposition
(FFT) is performed the harmonic distortion can be
measured. The amplitude of the 3rd harmonic (600
Hz) should be less then 1% of the fundamental
(200 Hz). It was measured to 1.2% (refer to
figure on the right). The signals are not "pure"
200 Hz sinusoids. If a spectral decomposition
(FFT) is performed the harmonic distortion can be
measured. The amplitude of the 3rd harmonic (600
Hz) should be less then 1% of the fundamental
(200 Hz). It was measured to 1.2% (refer to
figure on the right).
Data from Tektronic oscilloscope TDS210.
Calculated by Tektronix's WaveStar software.
|
| |
|
2. Platform control unit tests
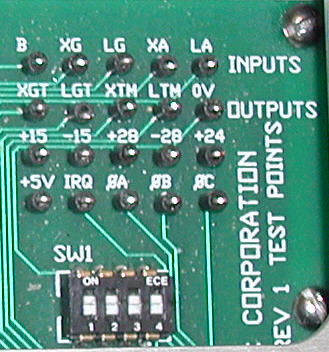
The testpoints are located on a small printed
circuit board inside the Platform Control Unit,
below the metal lid - see the figure to the
right.. Learn the "nomenclature" - it
makes testing easier:
X = Cross
L = Long
G = Gyro
A = Accelerometer
T = Torque
M = Motor
Note that "torque" applies to two
components: a) The motors that keep the platform
level, and b) the gyros, where the torque input
signal is used to compensate for long-term
horizontal reference changes (e.g. earth
rotation). If you're not aware of this it can be
a bit confusing.
Program switches SPRING TENSION and ALARM set
to OFF.
|
 |
| |
|
| No. |
Test-
points |
Ref. |
Scope
image |
Description |
| 1 |
B |
0V |
|
CPI sensor output, identical to front
panel meter. Slew the beam to end
positions.
Range: -9.8 Vdc .. 9.9 Vdc. |
| 2 |
XG |
0V |
Yes |
Cross Axis Gyro output signal
By turning off the Cross Torque Motor
switch you can see a 200Hz, 1V
peak-to-peak sine wave on an
oscilloscope, when the platform is
rotated in the cross axis direction.
Chooce IRQ as trigger for the
oscilloscope.
Multimeter (select AC measurements): 0.4
Vrms max. output. |
| 3 |
LG |
0V |
|
Long Axis Gyro output signal, similar
to XG. |
| 4 |
XA |
0V |
|
Cross Axis Accelerometer output.
By turning off the Cross Torque Motor
switch you can see a DC-voltage on an
oscilloscope or a voltmeter, when the
platform is rotated in the cross
direction.
Signal range: -12.6Vdc .. 11.9Vdc. |
| 5 |
LA |
0V |
|
Long Axis Accelerometer output,
similar to XA.
Signal range: -12.6Vdc .. 12.0Vdc. |
| 6 |
XGT |
0V |
Yes |
Cross Axis Gyro Torque - input signal
to gyro. Due to time integral this signal
build slowly to saturation.
Cross Torque Motor switch = OFF.
Signal range: -6.5 Vdc .. 8.7 Vdc |
| 7 |
LGT |
0V |
|
Long Axis Gyro Torque, similar to
XGT.
Signal range: -6.0 Vdc .. 8.2 Vdc |
| 8 |
XTM |
0V |
Yes |
Cross Axis Torque Motor. Signal to
motor that keeps platform level in cross
axis.
Cross Torque Motor switch = OFF.
Signal range: -1.6 Vdc .. 1.5 Vdc |
| 9 |
LTM |
0V |
|
Long Axis Torque Motor, similar to
XTM.
Signal range: -1.9 Vdc .. 1.6 Vdc |
| 10 |
IRQ |
0V |
Yes |
Interrupt Request. This is a digital
clock signal.
Only measure with oscilloscope!
Square wave, approx. 50% duty cycle, 200
Hz, 0-4V peak-to-peak. |
| 11 |
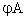 |
0V |
|
Gyro spin motor excitation voltage.
200 Hz, 24V peak-to-peak, 8.1V +/- 0.3V
rms.
> 40dB attenuation of 3rd harmonic
600Hz (means that 3rd harmonic's
amplitude should be less then 1% of 1st
harmonic's amplitude).
Note: Identical to
the Power Supply Unit testpoints! |
| 12 |
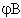 |
0V |
|
As Phase A, with 120║ phase shift. |
| 13 |
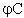 |
0V |
|
As Phase B, with 120║ phase shift. |
|
DC voltages ▒28V, ▒15, +24V, +5V can also be checked
via UltraSys program.
University
of Bergen
Institute of Solid
Earth Physics
AllÚ gt. 41, N-5007 Bergen, NORWAY
Tel: (+47) 5558 3420 / 21
Fax: (+47) 5558 9669
Email: elab@ifjf.uib.no
April 6, 2001 (OM)
|

 The signals are not "pure"
200 Hz sinusoids. If a spectral decomposition
(FFT) is performed the harmonic distortion can be
measured. The amplitude of the 3rd harmonic (600
Hz) should be less then 1% of the fundamental
(200 Hz). It was measured to 1.2% (refer to
figure on the right).
The signals are not "pure"
200 Hz sinusoids. If a spectral decomposition
(FFT) is performed the harmonic distortion can be
measured. The amplitude of the 3rd harmonic (600
Hz) should be less then 1% of the fundamental
(200 Hz). It was measured to 1.2% (refer to
figure on the right).
