
|
Surveys and data Instruments
Support to other department sections Support Dr. Scient. thesis Contribution to "Scientific infrastructure"
Obsolete, kept for reference
Last update: April 30, 2025, at 08:49 AM |
TIME CODED IMPULSE SEISMIC TECHNIQUEINTRODUCTION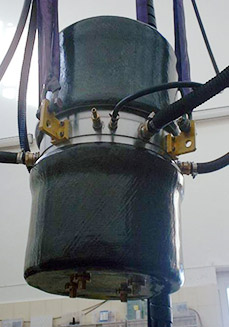 Low-frequency Acoustic Source (LACS), picture: Børge/Naxys webpage E-workshop performed large part of the fieldwork required by Dr. Bjørn Askeland's thesis work. Dr. Bjørn Askeland defended his thesis “Marine seismics with a Low-level Acoustic Combustion Source and time-coded sequences." 5 May 2008. Thesis background, quoting from SpringerLink Journal Article Abstract: "There has been a long-standing debate concerning how dangerous seismic surveys are with respect to marine life. Marine seismic work today is dominated by airgun technology, where high energy is generated by a release of compressed air into the water. The objective of the “Time coded impulse seismic technique” project is to examine whether a new low energy acoustic source can be used for seismic purposes. If the method turns out to be successful, the low output energy and continuous operation will make the source suitable in environmental sensitive areas. The Low level Acoustic Combustion Source (LACS) is a petrol driven pulsed underwater acoustic source. It operates at a few meters depth, and each shot can be digitally controlled from the surface by a computer located in the mother vessel. A presentation of the recorded LACS signal characteristics, the modulation, the Pseudo Noise coding/decoding principles and field test results, is given. The importance of using an optimized code with fine resolution and of using the near field recording as a correlator sequence is demonstrated. Clear correlation peaks could then be seen from the bottom and sub bottom reflectors."
Link to journal articles:
FIELDWORK DOCUMENTATIONSOME PICTURES Ship at Naxys premises, May 5 2004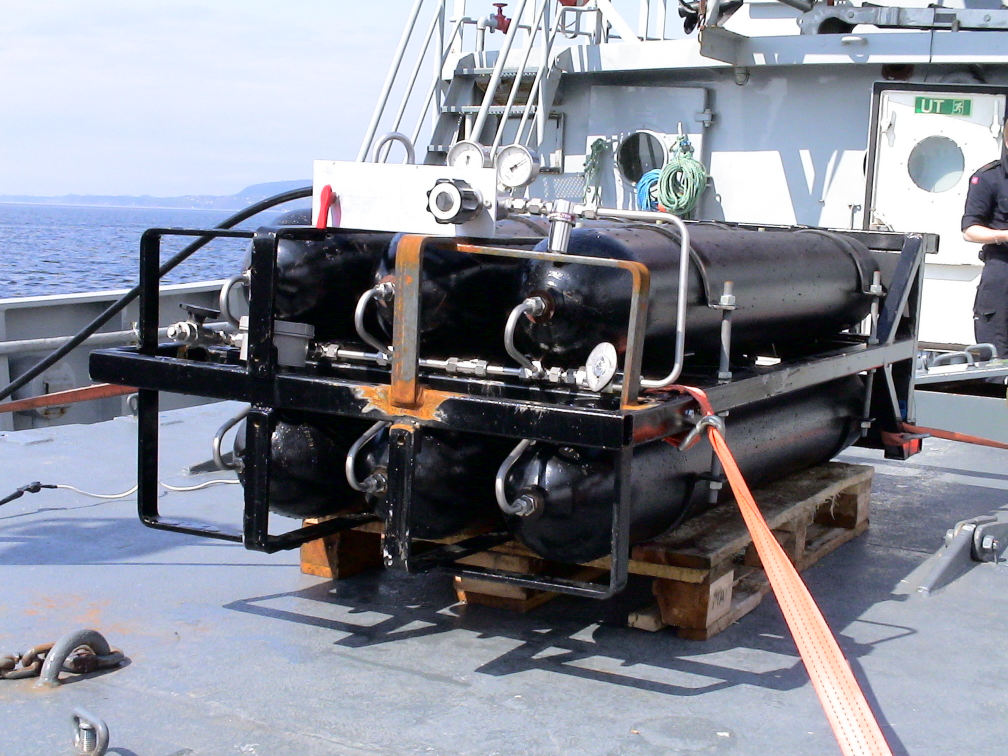  Compressed air battery, feeding airguns. |